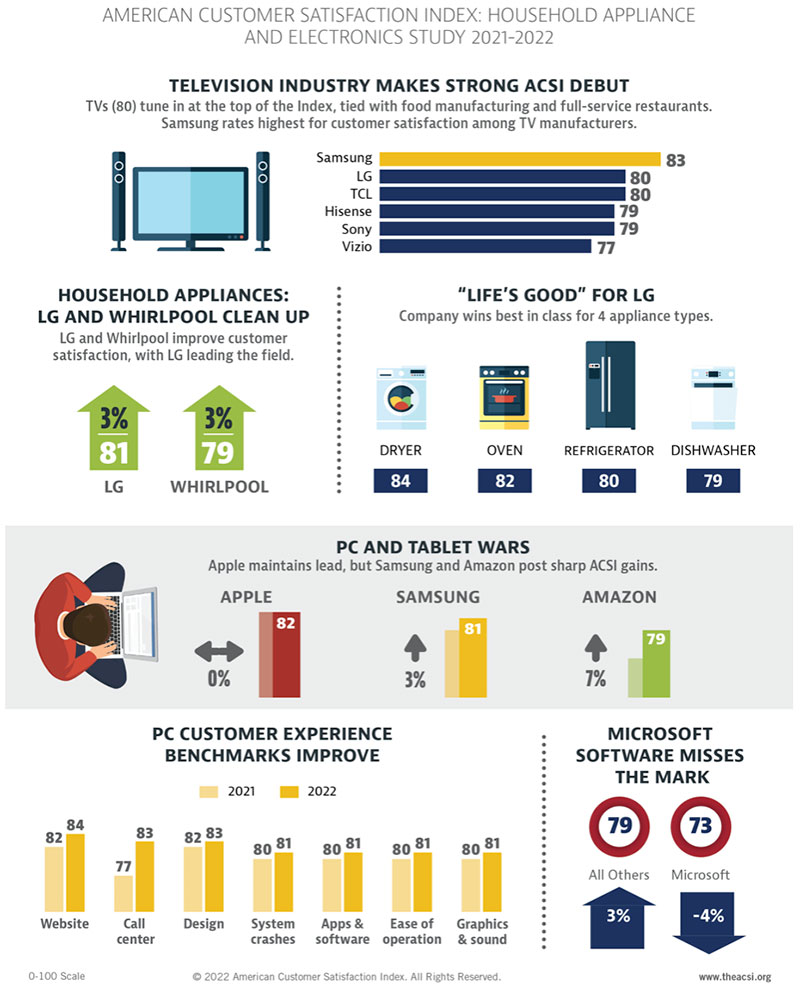
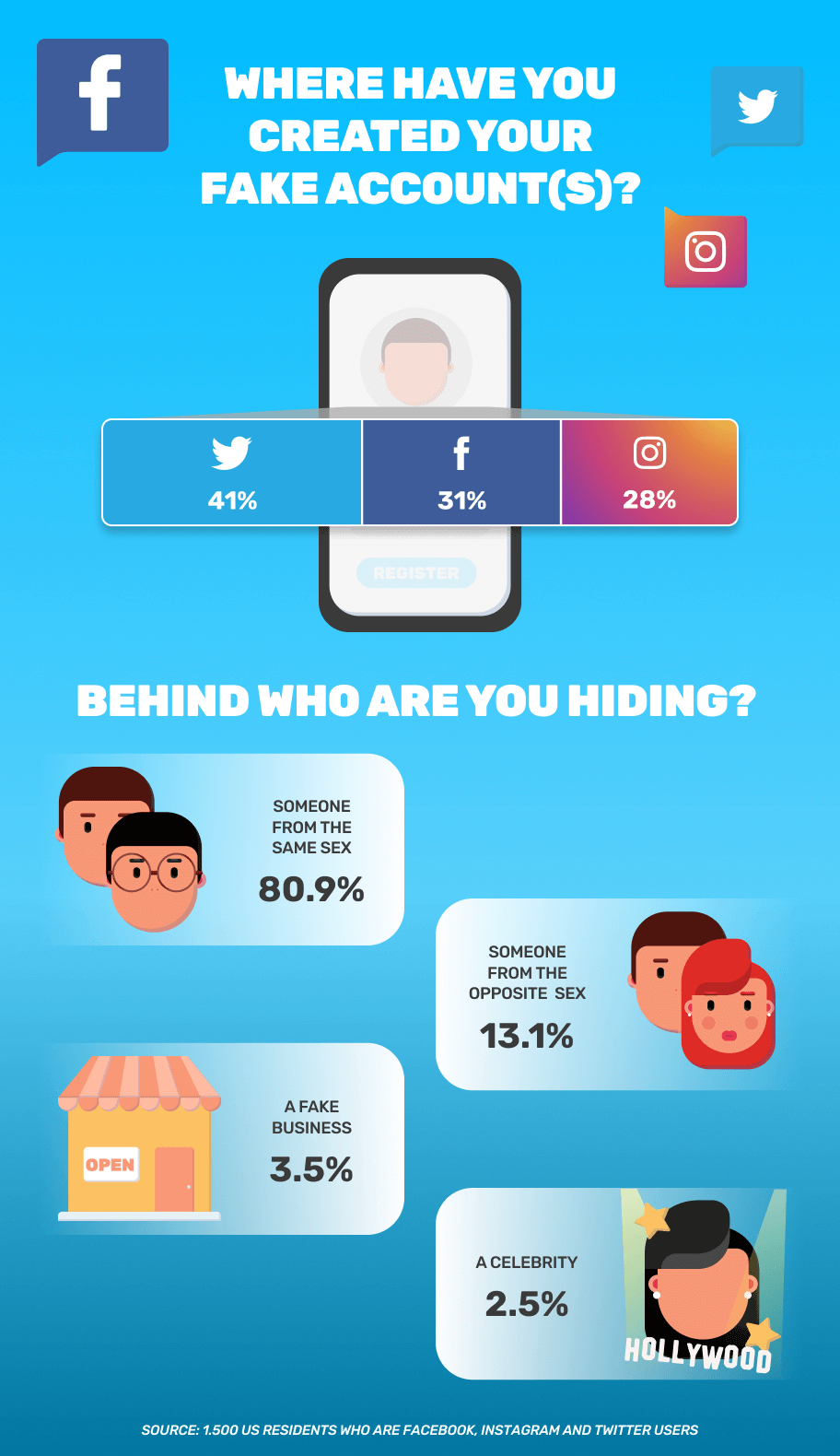
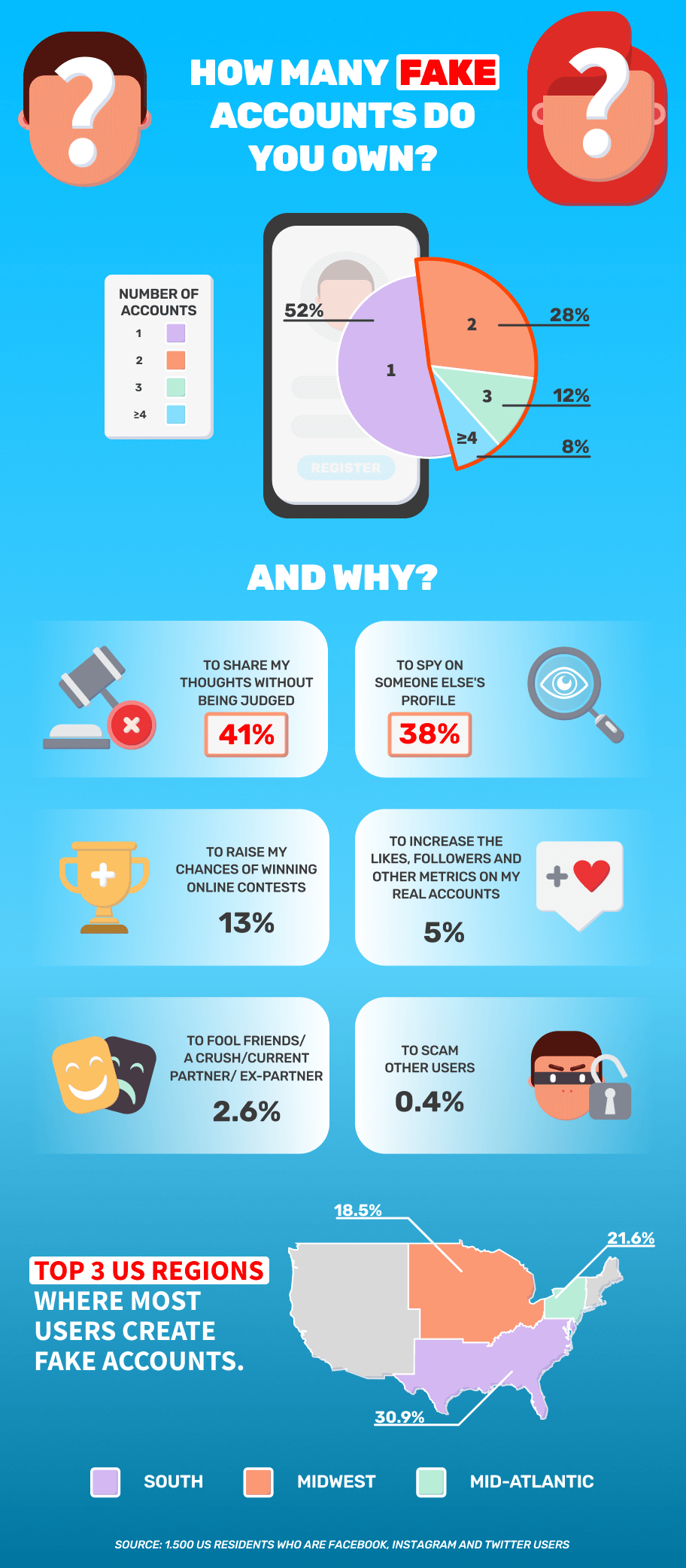
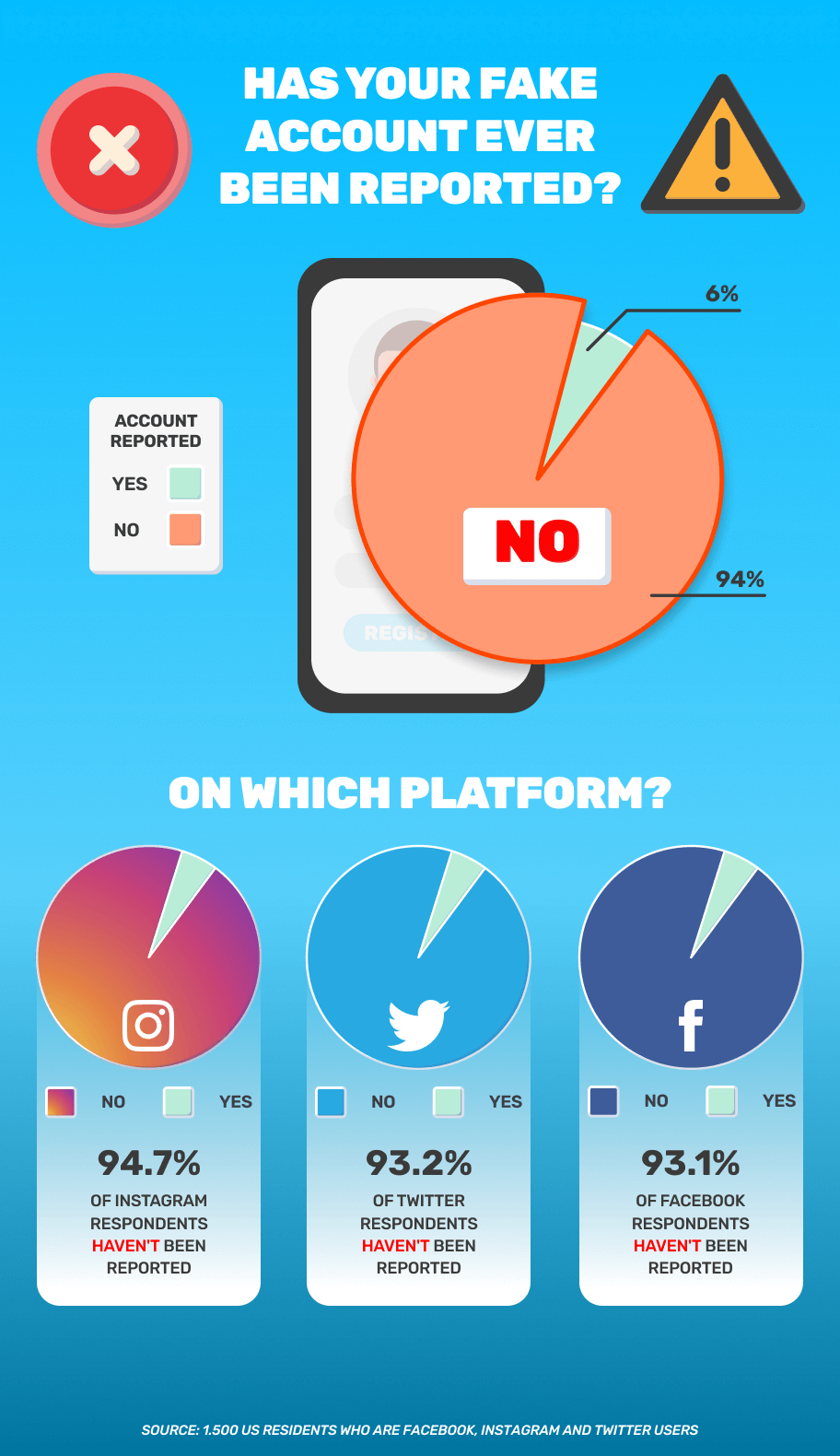
Advances in technology are spreading through law enforcement centers nationwide to help police departments better solve crimes and protect public safety. In this regard, law enforcement agencies are defined by some of the same gadgetry that is revolutionizing big business.
Technological advancement is driving reforms in neighborhood policing strategies and crime-fighting tactics. Some of these high-tech advancements have generated public and political concerns about privacy infringements and police behavior.
Typically, any change in government, school, and public policing operations confront challenges, doubts, and questions. Businesses, too, are often slow to adopt technological upgrades for some of the same factors, including cost.
Regardless of the organizations involved, technology brings change, both good and bad, despite the vetting process. Perhaps more so than in other industries, police departments nationwide face both internal and external concerns about implementing new high-tech options.
For example, some information technology (IT) tools are so innovative that courts have not had time to rule on their legality. When challenges are voiced, court processes take time. As rulings are issued, court decisions are often not applicable universally.
Police agencies nationwide are very involved with technology today, according to Mike Rodgers, CEO of Critical Response Group. CRG provides visual emergency operations plans to critical infrastructure that can be shared in real time with first responders during critical incidents.
“Police have to deal with the current threats facing our country and its communities. They have to deploy the best technology out there to give themselves the fighting edge when that opportunity presents itself,” he told TechNewsWorld.
We scoped out the broader view of how law enforcement is using technology for the common good.
Specialized Tools for Emergencies
Rodgers’ company is on the bleeding edge of innovation for law enforcement. It adapted high-end devices developed by U.S. forces on the battlefield to aid police departments in improving response and detection in high-stress emergency situations.
One of the most troublesome emergencies all police agencies face today, he offered, involves security and rescue in potential situations with active shooters. The Critical Response Group that Rodgers co-founded addresses that deadly situation with effective and innovative use of technology.
CRG is an indoor mapping company that transitions the lessons learned on the battlefield to public safety use at home, he noted. The process involved taking the military way of doing things with high-end mapping technology, so they were applicable to law enforcement procedures domestically.
We focus on providing the most accurate indoor mapping data that is compatible with what the tools public safety has employed today,” Rodgers said.
His company works with local law enforcement agencies throughout the U.S. to understand where each department is technologically. His team then integrates its mapping data directly into that existing structure. CRG also puts police officers on different mobile applications so they can leverage that technology from a mobile perspective, he explained.
“It’s more of a generational shift that public safety is being affected by where every person being hired on to a police department today has one if not two phones. They have used them for everything they have done for the last 10 years. So they’re bringing that skill set to public safety today,” said Rodgers.
Police work today is performed by officers who are more technical individuals out in the field. That technology trend is most evident with the New York Police Department, the largest law enforcement force in the world, he offered.
The NYPD is a first mover because of its resources. They recently moved all their officers off radios. Now every officer is using a cell phone.
“I think it is because they want to give the other officers the best possible chance when they are out there fighting crime, and you can do that with a portable [phone] and notebook [computer],” he said.
Battle-Tested, Best Practices
The CRG is comprised of former U.S. Special Operations Command operators who first used this solution on hundreds of real-world missions. Included within the CRG’s staff are domestic public safety experts who adapted these special teams’ tactics for use by first responders. The company employs a technical staff responsible for designing and managing collaborative mapping projects.
Rodgers’ company offers a solution based on what military units solved on the battlefield. A big problem law enforcement faces today with active shooter events is communication among responding agencies.
In these large-scale incidents, it is common for multiple police, ambulance, and fire departments to show up. Many times, the responding units come from other jurisdictions.
Everybody shows up. Everybody is on different communication systems. Post-incident response analysis repeatedly detailed such communication problems. That scenario was first discovered when the Twin Towers were struck by hijacked airlines in New York City.
The military figured out that with the war on terror they had to get everybody on basically one data-agnostic common operating picture, explained a CRG official. So they built out this communications system that all special forces units use when working on the same missions.
CRG takes the best practices for those units used overseas. What Rodgers’ company developed was essentially declassified technology brought to the U.S. as a domestic version.
Breaking Down Walled Information
CRG’s approach gives law enforcement a common solution to a nagging — and dangerous — situation. A common thread is that different law enforcement entities are terrible at sharing information.
One big factor in sharing information is everybody uses different databases and computer systems. Nobody’s computers talk to each other. So that is a direction for the future for law enforcement, observed Rodgers.
A glaring example of this is evident in New Jersey where CRG is based. The state has about 500 different police departments. They use dozens of records management systems and computer-aided dispatch systems.
Many departments do not regularly interface with each other. The result is a lot of separate, unconnected silos of information that create a major problem. The solution is finding a way to build almost data-agnostic systems on which everybody can share readily accessible information.
Mapping Data
Law enforcement is a very difficult, challenging environment right now. It is more complicated and complex than ever been, Rodgers noted.
Leveraging technology is the way police agencies can best deal with those issues. Mapping data is becoming the newest approach to dealing with high-tech solutions for law enforcement.
A graduate of the United States Military Academy at West Point, Rodgers left the army as a Captain after nine years of service and multiple combat deployments. His deployments included the 82nd Airborne Division, 75th Ranger Regiment, and Princeton University’s ROTC program.
His familiarity with using collaboration, interoperability, and information-sharing between all branches of the military, intelligence agencies, and coalition partners fueled his idea to form a company that does the same thing for first responders. The military approach created a communication technique called the Gridded Reference Graphic (GRG).
This is a visual communication tool that combines a grid overlay with high-resolution overhead imagery. That “big picture” enables all mission participants to communicate off a sheet of paper about unfamiliar locations.
The military’s GRG approach is used in every counter-terrorism mission conducted overseas. Its value rests in the ability to enable simple communication and collaboration for operators under stress in unfamiliar environments, according to the Critical Response Group.
In 2013, Rodgers began formulating the domestic version of that solution. He started the Rodgers Group. For the first couple of years, like anything new, growing his company was an uphill battle. Resistance to tearing down information silos within the law enforcement communities was one of his major roadblocks, he confided.
“People become comfortable in the way that they have always done things,” he added. Eventually, the concept behind his civilian solution for law enforcement gained traction.
Innovative Technologies for Law Enforcement
Three years later, Rodgers spun off what was a division within the Rodgers Group to form the Critical Response Group as a separate company partnered with the Rodgers Group. The goal was to transition and implement innovative technology and training techniques to enable better decisions faster and to ensure collaborative communication during critical incidents.
CRG developed three products to help law enforcement accomplish those goals. The company also facilitates Homeland Security Exercise and Evaluation Program (HSEEP)-compliant emergency response exercises, creates customized policies and training programs related to safety and security for public and private institutions, and provides security management programs for public and private facilities.
Collaborative Response Graphics are simple visual communication and collaboration tools. Usable under stress, they help to coordinate emergency response both outside and inside a building.
New High-Tech Tools Extend Options
Innovative tools for law enforcement and first responders that Rodgers’ companies developed are some of the newest high-tech options. Police organizations have been transitioning to tech-based solutions to improve or replace older technology.
Much of this high-tech advancement shares a similar thread. They all require high-level IT services integrated with big data. The key areas involve data mapping crime, tracking smartphones, keeping tabs on social media, relying on Wi-Fi, and using biometrics.
Many police departments either use body cameras already or plan to get them when budgeting permits. Body cameras serve a dual purpose. One, they document interactions between officers on the street and the citizens they encounter. Two, they provide evidence of how effective police training procedures are and where improvements are needed.
Drones offer the ability to perform aerial mapping, conduct high-level views of crime scenes, and help locate evidence. More sophisticated models are equipped with thermal imaging or 3D mapping software that brings GPS-enhanced precision to the areas being surveyed.
Also called unmanned aerial vehicles, or UAVs, police drones can carry zoom cameras. This added configuration increases their usefulness by delivering actionable, real-time information in high-risk situations. An added benefit is eliminating the need to arrange and wait for regional agencies to fly over in helicopters in emergency situations.
Issues related to police use of drones for surveillance has unresolved legal issues. But the positive benefits for police include the ability to locate suspects and citizens in distress more quickly.
In this regard, other high-tech gadgetry helps police officers change the law enforcement landscape for the better.
Cloud Support for Boots on the Ground
Cloud computing now turns once-isolated police vehicles into mobile data centers. Their extended communications reach solves the age-old problem of dealing with dead zones between police radio traffic and the dispatching center. Mobile phones also remove more limited communications capabilities police transmitters often entail.
It is not uncommon now for police officers alone in their vehicles to be constantly connected to real-time dashboards. The squad car of yesteryear has become a mobile comm center tethered to centralized criminal justice databases.
Wi-Fi-connected laptops, tablets, and in-dash computers allow police officers to remain in the field while they complete investigative reports and do essential database research.
This centralized data processing helps police agencies enhance public safety and better investigate criminal activity. Advanced computing resources assist with improved data management and compliance issues. These areas number among the most technologically challenging factors plaguing police in this high-tech age.
Older Tech Mixed With New
Two of the most well-known items “older” devices are Automatic License Plate Recognition (ALPR) and street surveillance cameras. ALPR technology has been used for 15 years and is utilized everywhere, not just in big cities. It has become an integral part of the traffic maintenance systems and locating scofflaws as camera and computer databases provide extended features.
Virtual reality is one of the newest tools in law enforcement. However, its use is still limited due to privacy regulations and related concerns. VR is the new classroom for improving how agencies handle tactical situations.
The Road Ahead
Today’s use of technology is better preparing law enforcement agencies to do their jobs more effectively and efficiently. Cutting ties with older, less capable equipment does not always go smoothly, pacify budget watchers, or assuage critics demanding the status quo.
Progressive policing agencies are starting to keep up with the high-tech curve. These agencies are paving the way for others unable or unwilling to move forward as rapidly.
Many agencies still struggle with issues identified in the 911 Commission Report, noted Rodgers. That is what his company is working hard to tackle.
Picture a law enforcement officer stepping out of the squad car to respond to a scene. The vest cam films the on-the-spot witness interviews and records all the conversations. The communications console in the vehicle relays everything back to the department’s cloud server. AI transcribes all the discourse, filters the appropriate details into a report, and packages the entire incident report to a centralized database that other agencies can instantly access.
Perhaps that is a picture for future police officers. But the technology is developing now to one day make that picture a reality.